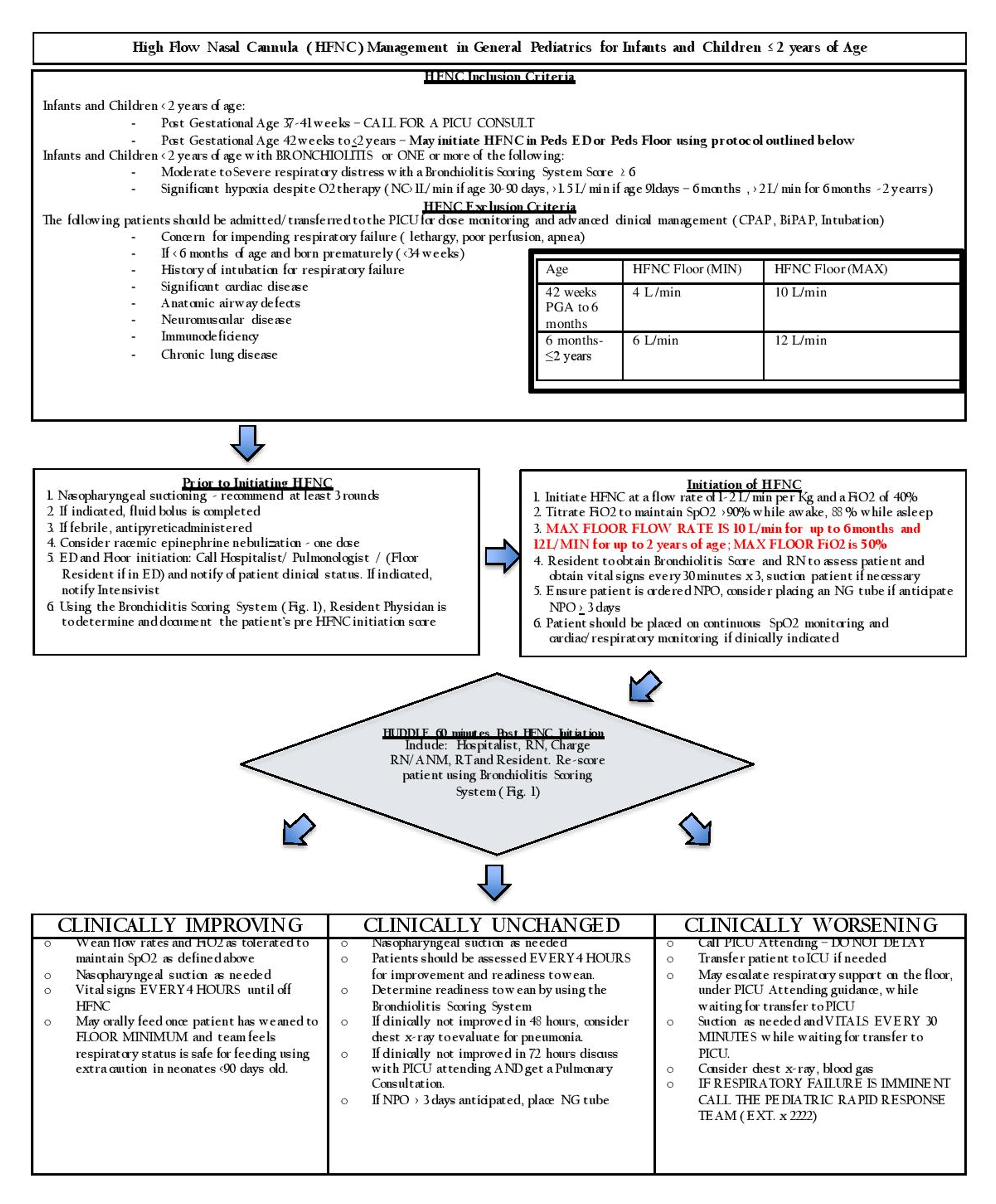
high flow nasal cannula flow rate pediatrics
High-flow gas is defined as a flow that meets or exceeds the patients inspiratory flow. Kawaguchi A Yasui Y deCaen A Garros D.
Outcomes And Protocol Overview High Flow Nasal Cannula Use In Bronchiolitis In Acute Care And Ed Vapotherm
21 hours agoNov 17 2022.

. Nasal High Flow for Infants and Children. The usage of high-flow nasal cannulas HFNC is on the rise in the pediatric population. The heat and humidified high-flow nasal cannula or as most call it high-flow nasal cannula HFNC isnt just a standard nasal cannula turned up to very high flow rates.
1 Without heated humidity the amount of gas flow delivered via nasal cannula is limited. Low flow nasal cannulas can only deliver a nasal cannula flow rate of 4-6 liters of oxygen per minute. N Engl J Med.
The global high flow nasal cannula market size was exhibited at USD 672837 million in 2022 and is predicted to hit USD 159264 million by 2030 growing at a CAGR of 113 during the. A nasal cannula set at 1Lmin flow rate can increase. High-flow humidified nasal cannula with optional supplementary oxygen delivery HFNC has evolved in recent years with a growing body of evidence of reduced.
Literature suggests that early and integrated use of Nasal High Flow NHF is key when implementing NHF in infants and children. So they often dry out the nasal. Download Citation Financial outcomes of high-flow nasal cannula use for bronchiolitis on the general pediatric floor High-flow nasal cannula HFNC is an.
There need to be more objective measures that can be used to predict. They dont provide humidified or heated oxygen. They can deliver up to 60 liters of.
Aim for oxygen saturation 88-92 for patients with a history of COPD until arterial. Bronchiolitis is one of the most common causes of pediatric emergency department ED use and hospitalization for children. A randomized trial of high-flow oxygen therapy in infants with bronchiolitis.
This topic will focus on the use of high-flow nasal cannula HFNC in pediatric patients including discussion of equipment proposed mechanisms of. They found that breathing efforts decreased as flow rates increased with the largest decrease at a flow rate of 2 Lkg per minute in infants suggesting that lower flow rates.
Cureus The Use Of High Flow Nasal Cannula And The Timing Of Safe Feeding In Children With Bronchiolitis
When Hfnc Is Not Enough For Your Babies And Why High Velocity Therapy Could Help Vapotherm

High Flow Nasal Cannula Use In Children With Bronchiolitis In A Community Hospital Setting Evaluation Of Safety Flow Limits And Intensive Care Unit Transfers The Permanente Journal
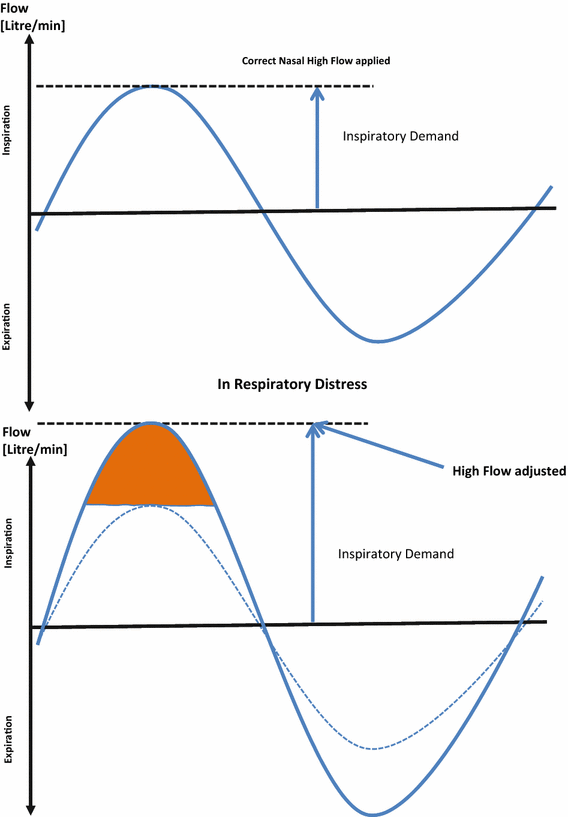
Glass Half Empty Or Half Full The Story Of High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Critically Ill Children Springerlink

Optimal Rate Of Flow For High Flow Nasal Cannula In Young Children The Hospitalist
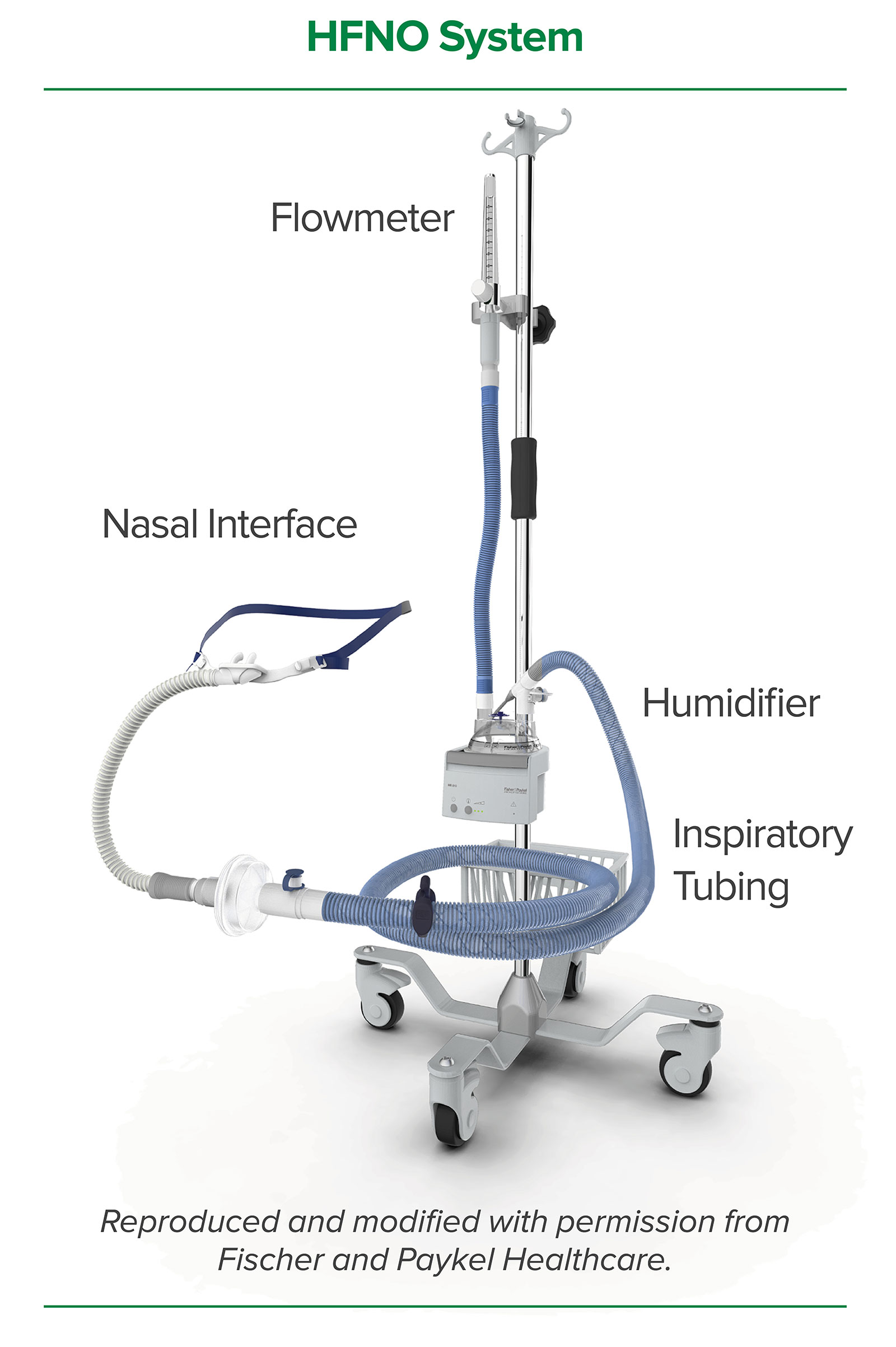
Safe Use Of High Flow Nasal Oxygen Hfno With Special Reference To Difficult Airway Management And Fire Risk Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation

Pdf High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy In Children A Clinical Review Semantic Scholar

High Flow Therapy When And How Don T Forget The Bubbles

Characteristics And Outcome Of High Flow Nasal Cannula Episodes Download Table
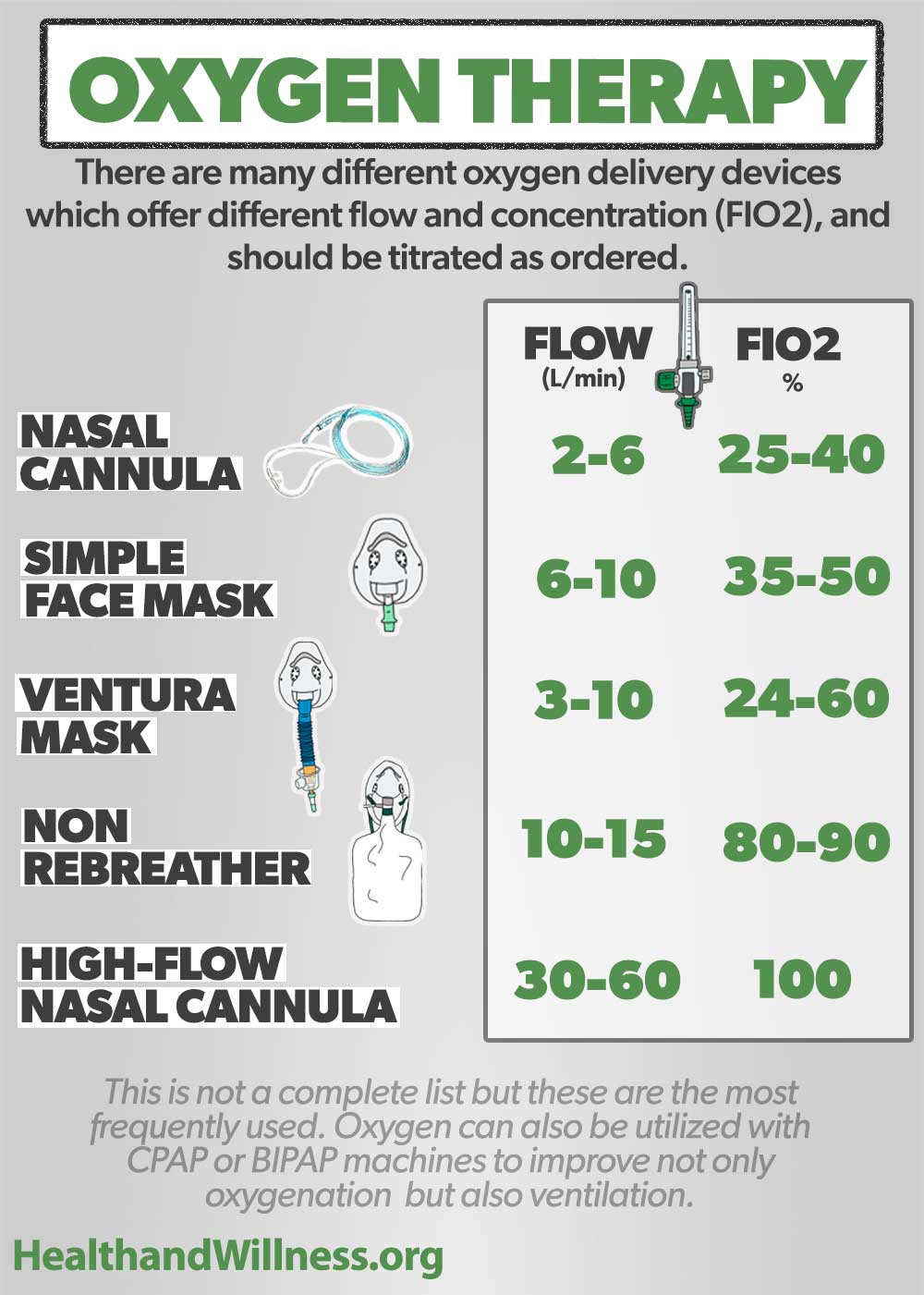
Oxygen Delivery Devices And Flow Rates Health And Willness

Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Children Archives Of Disease In Childhood

Initial Or Starting Flows Of High Flow Nasal Cannula In A Pediatric Download Table
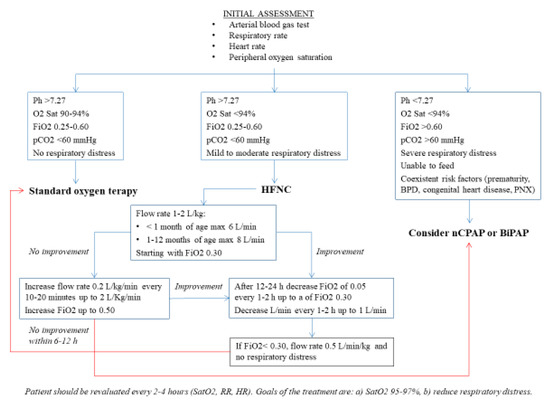
Children Free Full Text Update On The Role Of High Flow Nasal Cannula In Infants With Bronchiolitis Html
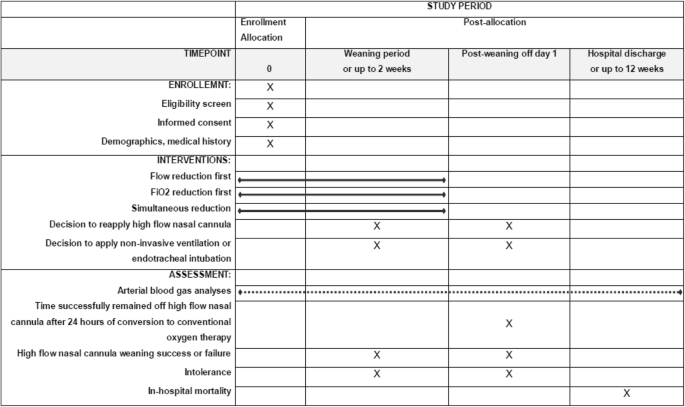
Simultaneous Reduction Of Flow And Fraction Of Inspired Oxygen Fio2 Versus Reduction Of Flow First Or Fio2 First In Patients Ready To Be Weaned From High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Study Protocol
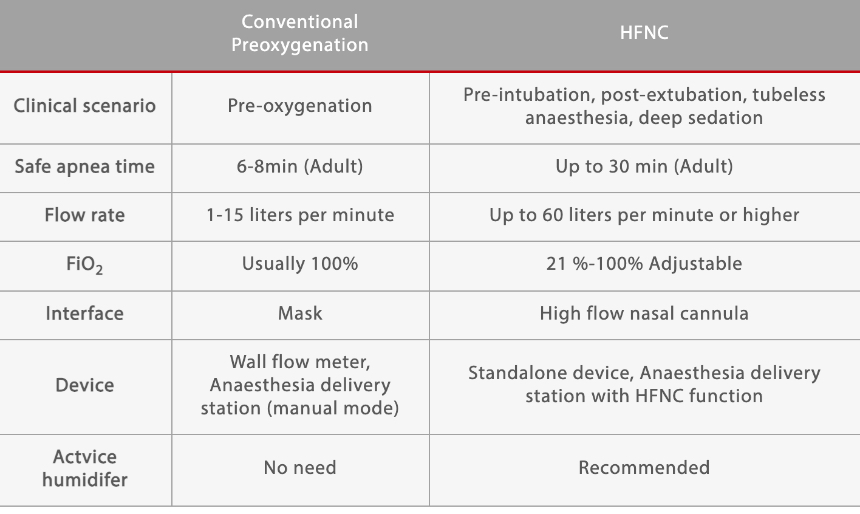
High Flow Nasal Cannula Hfnc Oxygen In Anaesthesia Mindray Global

Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy And Noninvasive
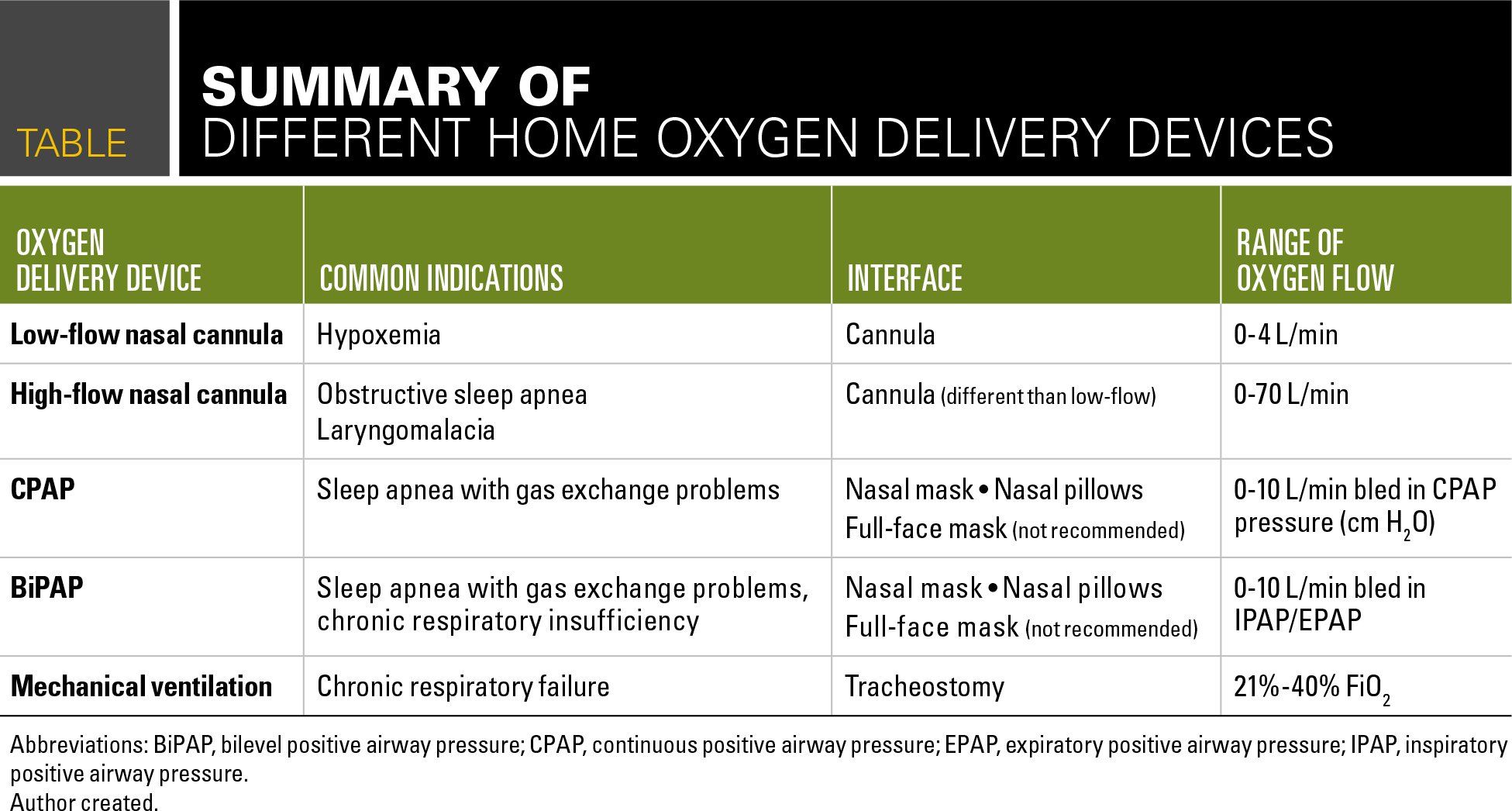
Oxygen Delivery In The Home Setting

Pdf Association Between High Flow Nasal Cannula And End Expiratory Esophageal Pressures In Premature Infants Semantic Scholar

Physiological Responses And Perceived Comfort To High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Awake Adults Effects Of Flow Magnitude And Temperature Journal Of Applied Physiology